An indirect tax is a tax applied on the manufacture or sale of goods and services. There are two types of indirect taxes – ad valorem tax and specific tax. A specific tax is imposed on each unit, i.e. $0.50 on a pack of cigarettes, while an ad valorem tax (or percentage tax) is a percentage of the price like a sales tax of 10%. For example, cities in California have a sales tax that ranges from 7.25% to 10.50%. Indirect taxes discourage the consumption of goods and services and are represented by a decrease in supply.
Contents
show
Types of Indirect Taxes
Ad Valorem Tax
Specific Tax
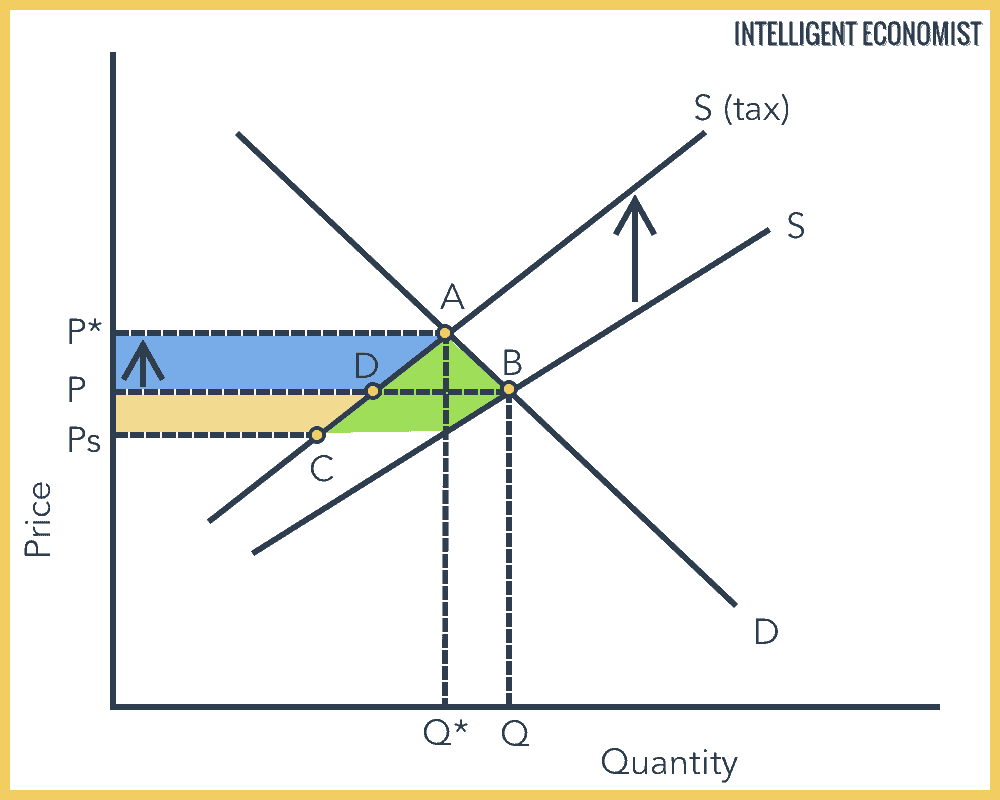
Effects of Indirect Taxes
- The Supply shifts or falls from S to S(tax)
- The Quantity consumed falls from Q to Q*
- The Price paid by the consumer increases from P to P*
- The Revenue collected by the producer falls from PBQ0 to PsCQ*0
The Tax Burden
- The Green box is tax revenue paid by the producer
- The Blue box is tax revenue paid by the consumer
- The government collects the blue and green box
- The red triangle ABC is welfare loss to society (specific tax), as a result of a fall in consumer and producer surplus
Arguments for Indirect Tax
- Indirect taxes can be used to make the polluter pay and internalize the external costs of production and consumption.
- Changes in indirect taxes can change the pattern of demand. This taxation policy is useful if the government wants to discourage the consumption of a particular good.
- Indirect taxes are less easy to avoid. This ensures that the entire population pays some form of tax. In the case of direct taxes (like income tax), the poor are not taxed due to their low income.
Arguments Against Indirect Tax
- Indirect taxes make the distribution of income more unequal because of their regressive effects. The poor will get taxed a higher proportion of their income than the rich, making it a regressive tax.
- Higher indirect taxes can cause cost-push inflation which can lead to a rise in inflation expectations.
- Revenue from these taxes can be uncertain when inflation is low or there is a recession causing a fall in consumer spending.


The graphics included in this article are really great!
this was so informative and great.but could you please post more like how indirect tax can be used to reduce consumption of a demerit good. still as I said your work is really impressive